Cotton Wool Detection for Diabetic Retinopathy
Computer Vision for Early Detection of Diabetic Eye Disease
Overview
This computer vision project focuses on detecting cotton wool spots in retinal images for early detection of diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of vision loss in diabetic patients. The project employs advanced image processing and machine learning techniques to identify and classify cotton wool spots in fundus images.
Background
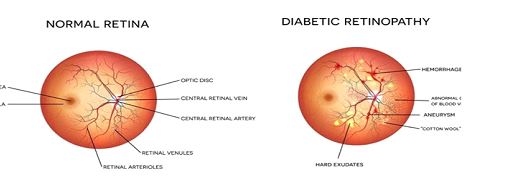
Diabetic Retinopathy
- Leading cause of blindness in working-age adults
- Affects millions of diabetic patients worldwide
- Early detection is critical for preventing vision loss
- Cotton wool spots are key indicators of disease progression
Clinical Significance
Cotton wool spots (soft exudates) are:
- Small, fluffy white lesions in the retina
- Indicative of nerve fiber layer infarctions
- Important biomarkers for diabetic retinopathy severity
- Early warning signs requiring medical attention
Methodology
Image Processing Pipeline
- Preprocessing
- Retinal image enhancement
- Noise reduction and contrast adjustment
- Image normalization
- Feature Extraction
- Texture analysis
- Color space transformation
- Edge detection
- Morphological operations
- Detection Algorithm
- Machine learning-based classification
- Pattern recognition for cotton wool spots
- ROI (Region of Interest) identification
Technologies Used
- Computer Vision: OpenCV for image processing
- Programming: Python
- Machine Learning: Scikit-learn for classification
- Image Processing: Advanced filtering and segmentation techniques
Detection results showing identified cotton wool spots in retinal images.
Key Features
- Automated detection of cotton wool spots
- High accuracy in classification
- Suitable for screening applications
- Potential for integration into diagnostic tools
Impact
- Healthcare: Assists ophthalmologists in diagnosis
- Screening: Enables large-scale diabetic retinopathy screening
- Early Detection: Helps prevent vision loss
- Cost-Effective: Reduces manual examination burden
Project Details
Institution: Jain University, Bangalore
Department: Electronics & Communication Engineering
Supervisor: Prof. Chethan GS
Year: April 2024
Type: Minor Project Research
Technical Challenges Addressed
- Variability in image quality
- Complex retinal background
- Similar-looking features (false positives)
- Real-time processing requirements
Results
- Successful detection of cotton wool spots
- Robust performance across diverse fundus images
- Demonstrated feasibility for clinical application
- Foundation for further medical imaging research
Future Enhancements
- Deep learning models (CNNs) for improved accuracy
- Multi-class classification (different retinopathy stages)
- Mobile application for point-of-care diagnosis
- Integration with electronic health records
- Larger dataset validation