Human Voice Recognition System
Feed Forward Neural Networks for Speaker Recognition
Overview
This project implements an advanced human voice recognition system using feed forward neural networks for speaker identification and verification platforms. The system leverages deep learning and digital signal processing techniques to achieve high accuracy in voice recognition tasks.
Project Objectives
- Develop robust speaker recognition system
- Achieve high accuracy in voice identification
- Minimize Equal Error Rate (EER)
- Create platform-independent solution
Technical Approach
Digital Signal Processing
Feature Extraction Methods:
- MFCC (Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients)
- Standard feature for speech recognition
- Captures spectral envelope information
- Mimics human auditory perception
- FBANK (Filter Bank Features)
- Complementary to MFCC
- Preserves more spectral information
- Useful for neural network input
Deep Learning Architecture
Feed Forward Neural Networks:
- Multi-layer perceptron architecture
- Optimized for voice pattern recognition
- Trained on extracted audio features
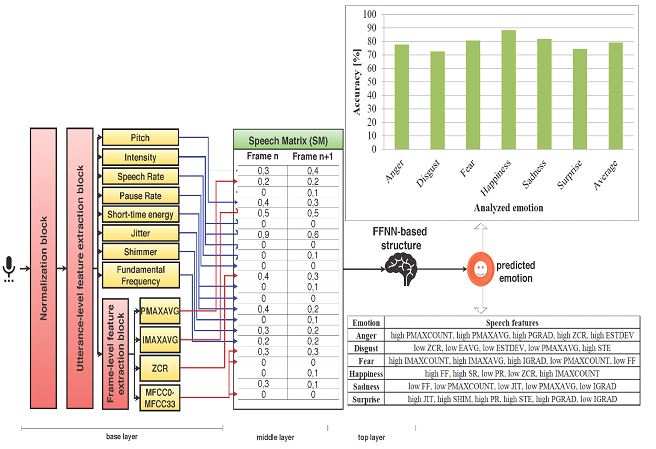
Implementation Details
Technology Stack
- Programming Language: Python 3
- Deep Learning Frameworks: PyTorch, TensorFlow, Scikit-learn
- Signal Processing: NumPy, Librosa
- Audio Analysis: Digital signal processing libraries
System Pipeline
- Audio Input: Capture or load voice samples
- Preprocessing: Noise reduction, normalization
- Feature Extraction: MFCC/FBANK computation
- Neural Network: Feed forward classification
- Output: Speaker identification/verification
Performance Metrics
Evaluation Criteria
- Accuracy: Overall classification correctness
- F1-Score: Balanced precision and recall
- EER (Equal Error Rate): System reliability metric
- Lower EER indicates better performance
- Critical for security applications
Results
- High accuracy compared to traditional methods
- Low Equal Error Rate (EER)
- Robust performance across different speakers
- Significant improvements over baseline systems
Applications
Security & Authentication
- Biometric access control
- Voice-based authentication
- Secure banking systems
User Experience
- Voice assistants personalization
- Smart home automation
- Adaptive user interfaces
Enterprise Solutions
- Call center verification
- Forensic analysis
- Customer service automation
Research Contribution
Master’s Thesis
Institution: National School of Engineering (ENI-ABT), Bamako, Mali
Supervisor: Dr. Abdoulaye Sidibe
Period: 2019-2020
Technical Innovations
- Hybrid Feature Approach: Combined MFCC and FBANK features
- Optimized Network Architecture: Tuned for voice recognition
- Efficient Processing: Real-time capable implementation
- Cross-Platform: Platform-independent design
Challenges & Solutions
Challenge 1: Background Noise
Solution: Advanced preprocessing and noise reduction algorithms
Challenge 2: Speaker Variability
Solution: Extensive training on diverse voice samples
Challenge 3: Computational Efficiency
Solution: Optimized neural network architecture
Challenge 4: Feature Selection
Solution: Combined MFCC and FBANK for comprehensive representation
Code & Implementation
- Modular Python codebase
- Well-documented functions
- Reusable components
- Extensible architecture
Future Enhancements
- Deep neural networks (RNNs, CNNs)
- Larger training datasets
- Multi-language support
- Real-time mobile implementation
- Cloud-based recognition service
- Continuous learning capability
Technologies Demonstrated
- Deep Learning (PyTorch, TensorFlow)
- Signal Processing (NumPy, Librosa)
- Audio Analysis
- Pattern Recognition
- Machine Learning (Scikit-learn)
- Python Development